Measuring Two Decades of Urban Spatial Structure: The Evolution of Agglomeration Economies in American Metros
Abstract
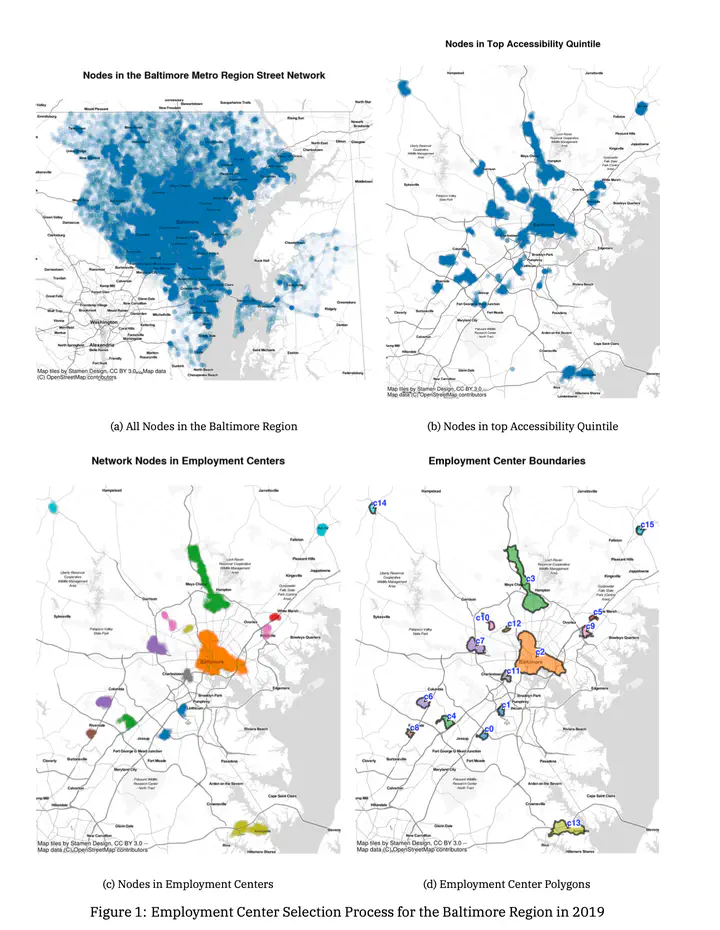
In this paper we examine the evolution of urban spatial structure in U.S. metropolitan areas over nearly two decades. Using annual block-level data from the Longitudinal Employment Household Dynamics database, we introduce a technique for identifying regional employment centers that both adheres to urban economic theory and pays homage to classic contributions in local spatial statistics. Centers are defined as local spatial statistical outliers on the network-based job accessibility surface. We proceed by identifying the location and employment makeup of centers for each metropolitan region in the USA from 2002 to 2019 and discuss emergent trends across time and space. Critically, we not only explore empirical patterns, but we discuss the relationship between polycentricity, the evolution of urbanization and localization economies, and regional specialization. We confirm again the pattern of polycentricity in U.S. metros and show that the structure of metropolitan employment is largely stable over time. We also document a continuing trend away from urbanization economies into more specialized subcenters.